analyzing exonuclease-induced hyperchromicity by uv spectroscopy|Analyzing Exonuclease : mail order - "Analyzing Exonuclease-Induced Hyperchromicity by UV Spectroscopy: An Undergraduate Biochemistry Laboratory Experiment" Figure 2. Secondary structure with the lowest free energy as predicted by RNAstructure.15,16 Probability refers to the probability of finding that base in that specific interaction and structure element. Resultado da Configuração service. Gerar token de acesso. Verificar acesso API. Configurando acesso API Apache. Configurando acesso API Nginx. .
{plog:ftitle_list}
webGarotas de programa São Vicente. As melhores acompanhantes São Vicente e garotas de programa que te oferecem grande variade de serviços eróticos. Etre em contato com as .
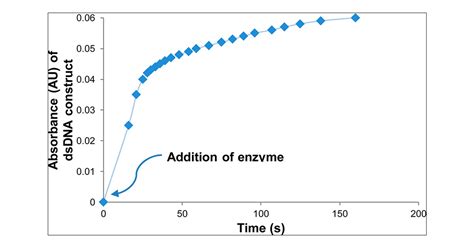
An undergraduate biochemistry laboratory experiment is described that utilizes free online bioinformatics tools along with readily available exonucleases to . Analyzing Exonuclease-Induced Hyperchromicity by UV Spectroscopy: An Undergraduate Biochemistry Laboratory Experiment. This experiment utilizes exonuclease .exonuclease is added to the solution containing the DNA, the strand is digested and the interactions disappear, leading to an increase in the absorbance called hyperchromicity. This .UV absorbance of double-stranded DNA at the ?[subscript max] is decreased when the DNA bases are involved in hydrogen bonding and formation of secondary structure. When an exonuclease is added to the solution containing the DNA, the strand is digested and the interactions disappear, leading to an increase in the absorbance called hyperchromicity.
- "Analyzing Exonuclease-Induced Hyperchromicity by UV Spectroscopy: An Undergraduate Biochemistry Laboratory Experiment" Figure 2. Secondary structure with the lowest free energy as predicted by RNAstructure.15,16 Probability refers to the probability of finding that base in that specific interaction and structure element.Figure 3. Single-stranded DNA hyperchromicity in 0.25 and 0.50 μM DNA samples (both with 1 μL of enzyme) and 1.25 μM DNA/(3 μL of enzyme). The x-axis has been truncated from 600 to 150 s in this figure and in Figures 4−6 for .
UV absorbance of double-stranded DNA at the ?[subscript max] is decreased when the DNA bases are involved in hydrogen bonding and formation of secondary structure. When an exonuclease is added to the solution containing the DNA, the strand is digested and the interactions disappear, leading to an increase in the absorbance called hyperchromicity.
Đường cong nóng chảy của axit nucleic cho thấy tính siêu âm là một hàm của nhiệt độ. Hyperchromicity là sự tăng độ hấp thụ (mật độ quang) của vật liệu.Ví dụ nổi tiếng nhất là tính siêu âm của DNA xảy ra khi song ánh DNA bị biến tính. [1] Sự hấp thụ tia cực tím tăng lên khi hai chuỗi DNA đơn lẻ được tách .UV absorbance of double-stranded DNA at the ?[subscript max] is decreased when the DNA bases are involved in hydrogen bonding and formation of secondary structure. When an exonuclease is added to the solution containing the DNA, the strand is digested and the interactions disappear, leading to an increase in the absorbance called hyperchromicity.C.M. Chant, “Analyzing Exonuclease-Induced Hyperchromicity by UV Spectroscopy – An Undergraduate Biochemistry Laboratory,” oral presentation abstract accepted for presentation at the Biennial Conference on Chemical Education (BCCE Biochemistry Laboratory Symposium), University of Northern Colorado, Colorado, August 2016.UV absorbance of double-stranded DNA at the ?[subscript max] is decreased when the DNA bases are involved in hydrogen bonding and formation of secondary structure. When an exonuclease is added to the solution containing the DNA, the strand is digested and the interactions disappear, leading to an increase in the absorbance called hyperchromicity.
UV absorbance of double-stranded DNA at the λ max is decreased when the DNA bases are involved in hydrogen bonding and formation of secondary structure. When an exonuclease is added to the solution containing the DNA, the strand is digested and the interactions disappear, leading to an increase in the absorbance called hyperchromicity.An undergraduate biochemistry laboratory experiment is described that utilizes free online bioinformatics tools along with readily available exonucleases to study the effects of base stacking and hydrogen bonding on the UV absorbance of DNA samples. UV absorbance of double-stranded DNA at the λmax is decreased when the DNA bases are involved in hydrogen . The profile of UV absorbance versus temperature is called a melting curve and the midpoint of the transition is defined as the melting temperature, Tm. . Analyzing Exonuclease-Induced Hyperchromicity by UV Spectroscopy: An Undergraduate Biochemistry Laboratory Experiment . Variable temperature NMR spectroscopy is used to determine the ΔH . A few experiments involving the application of spectroscopy to the determination of thermodynamic properties have been published in this Journal. . Analyzing Exonuclease-Induced Hyperchromicity .
An undergraduate biochemistry laboratory experiment is described that utilizes free online bioinformatics tools along with readily available exonucleases to study the effects of base stacking and hydrogen bonding on the UV absorbance of DNA samples. UV absorbance of double-stranded DNA at the λmax is decreased when the DNA bases are involved in hydrogen .
Información del artículo Analyzing Exonuclease-Induced Hyperchromicity by UV Spectroscopy: . UV absorbance of double-stranded DNA at the λmax is decreased when the DNA bases are involved in hydrogen bonding and formation of secondary structure. When an exonuclease is added to the solution containing the DNA, the strand is digested and the .into its single-stranded components. As UV-Visible absorption spectroscopy is a non-destructive technique, this analysis can be carried out using samples which can be further analyzed later. In an ideal scenario, the resulting sigmoidal curve, as shown in Figure 3, should be observed, where no change is observed Analyzing Exonuclease-Induced Hyperchromicity by UV Spectroscopy: An Undergraduate Biochemistry Laboratory Experiment. Journal of Chemical Education 2016 , 93 (12) , 2089-2095. Most UV-vis instruments can analyze solid samples or suspensions with a diffraction apparatus (Figure \(\PageIndex{7}\)), but this is not common. UV-vis instruments generally analyze liquids and solutions most efficiently. Figure \(\PageIndex{7}\) Schematic representation of the apparatus for collecting UV-vis spectra from solid materials.
Ultraviolet-visible (UV-Vis) spectroscopy is a widely used technique in many areas of science ranging from bacterial culturing, drug identification and nucleic acid purity checks and quantitation, to quality control in the beverage industry and chemical research. This article will describe how UV-Vis spectroscopy works, how to analyze the output data, the technique's .Hyperchromicity is the increase of absorbance (optical density) of a material.The most famous example is the hyperchromicity of DNA that occurs when the DNA duplex is denatured. [1] The UV absorption is increased when the two single DNA strands are being separated, either by heat or by addition of denaturant or by increasing the pH level. The opposite, a decrease of . 1.8.4 Electronic Spectroscopy of Proteins. The observed UV/visible spectrum in the case of peptides and proteins is determined by the spectroscopy of the amide bonds, the side chains, and any prosthetic groups (such as hemes) . The UV absorption spectra of proteins are categorized into two groups, namely the “far” and “near” UV regions.Hyperchromicity is the increase of absorbance (optical density) of a material.The most famous example is the hyperchromicity of DNA that occurs when the DNA duplex is denatured. [1] The UV absorption is increased when the two single DNA strands are being separated, either by heat or by addition of denaturant or by increasing the pH level. The opposite, a decrease of .
Water resources are closely linked to human productivity and life. Owing to the deteriorating water resources environment, accurate and rapid determination of the main water quality parameters has become a current research hotspot. Ultraviolet-visible (UV-Vis) spectroscopy offers an effective tool for qualitative analysis and quantitative detection of contaminants in a water . We report on ultraviolet (UV) light induced increases in the UV optical density of thin and optically transparent crystalline DNA films formed through self assembly. The films are comprised of .
Beckman DU640 UV/Vis spectrophotometer. Ultraviolet (UV) spectroscopy or ultraviolet–visible (UV–VIS) spectrophotometry [1] [2] [3] refers to absorption spectroscopy or reflectance spectroscopy in part of the ultraviolet and the full, adjacent visible regions of the electromagnetic spectrum. [2] Being relatively inexpensive and easily implemented, this methodology is widely .
The DPPH assay is a well-known method which is frequently employed as it is simple, has a low cost, requires little operator skills, and uses a simple spectrophotometer [1].It has been applied to quantify antioxidant activity in food, plant extracts, and beverages [2, 3] using antioxidant standards as ascorbic acid (AscH 2), butylated hydroxyl toluene (BHT), α .
High Frequency wood moisture meter warehouse
Analyzing Exonuclease
11/03/2023. Cozinheira morre no primeiro dia de trabalho após panela de pressão explodir. VEJA VÍDEO. Foto: Reprodução. Acidente ocorreu na noite de quinta-feira, em uma .
analyzing exonuclease-induced hyperchromicity by uv spectroscopy|Analyzing Exonuclease